What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is not just tech jargon anymore. It is the backbone of how the modern world runs. In the olden days, if you wanted to run a business, store files, or launch an app, you had to buy servers, hire IT teams, and ensure your hardware didn’t crash. Now? All you need is a solid internet connection, and you get access to powerhouses like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud at your fingertips with cloud computing architecture, making it fast, reliable, and secure. In simple terms, cloud computing means using the internet to access computing services, be it storage, servers, apps, or databases. You no longer need to store everything on your machine, as the cloud holds it for you, keeps it updated, while allowing easy access from all locations. If we talk about its five basic traits, cloud computing provides you with network flexibility, on-demand access, resource sharing, instant scaling, and pay-as-you-go pricing. Thus, cloud computing is the utility model for the Internet era. Whether you handle big business or are a solo developer, you get access to the same tools. So, the democratic access to powerful technology enables innovation at every scale, be it from startups to global enterprises. The cloud isn’t the future, it is the ‘now’!
How does Cloud Computing work?
With cloud hosting, you don’t buy the hardware, build the infrastructure, or monitor a server room. Instead, cloud infrastructure allows you to rent power, storage, and software from giants like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud, handling the operations behind the scenes. As a user, you tap into a shared pool of virtualized resources hosted by these cloud service providers (CSPs). This system is a network of remote data centers, with servers, databases, and networking tools, distributed across the globe. And, these data centers are equipped with storage racks, security protocols, and non-stop cooling systems, all fine-tuned to keep your data fast, safe, and online 24/7. On the surface, it feels easy. You open Google Docs, or maybe your photos quietly back up to iCloud without you lifting a finger. But behind all that, there is a whole squad of virtual machines, servers, and behind-the-scenes plays happening in real time. That is when cloud architecture carries out the functions. Up front, it is just your apps, your browser, and your phone. But they feed into the back end, where the real action is happening. A central server runs the show, backed by middleware. One physical server can spin up multiple virtual machines, each handling a different task or user. It allows the cloud to be flexible while sharing resources and adapting quickly.
Basic Principles of Cloud Technologies
As mentioned above, the cloud computing services are delivered by CSPs. And, you can easily purchase it as a subscription with services hosted, maintained, and managed by the CSP. The key services typically include IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, as each of these has its own level of CSP and customer involvement. The foundational principles of cloud technologies keep things fast, secure, and on the go. You can handle apps remotely and migrate from one site to another, while everything stays connected. If you need freedom to switch, integrate, or expand, everything happens with zero friction. Moreover, isolation is a non-negotiable principle of cloud computing as it prevents unauthorised access. You are sharing infrastructure, not your data. Cloud also gives you easy elasticity and scalability, allowing your systems to adjust in real-time to traffic. You do not have to adjust to one-size-fits-all in the cloud. It creates tailor-made solutions for you, all of which are backed by trust. Besides this resource pooling, on-demand self-service, and broad access, the cloud is what’s next.
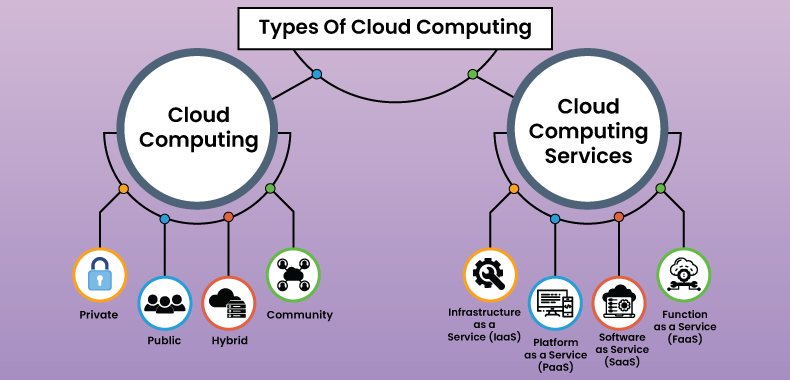
Different Types of Cloud Computing
Public Cloud Computing
Public cloud computing is a deployment model in which third-party providers offer computing resources over the public internet. So the CSPs have already built the infrastructure, and you rent what you need. It is a pay-as-you-go, scale-as-you-grow model. No setup delays, no maintenance headaches. You get on-demand access, broad device support, auto-scaling, and transparent billing with public cloud computing.
Private Cloud Computing
Private cloud computing is for those who want total control, tight security, and zero resource sharing, without any neighbors. While public cloud users split resources and trust someone else with their data, private cloud infrastructure allows you to pick hardware, software, firewalls, and the security stack. And if you are operating on locked-down networks, it gives you fast, stable performance with privacy.
Hybrid Cloud Computing
Hybrid cloud computing blends public and private cloud (and sometimes your old-school on-prem setup) into one connected system. Hence, you can move data and apps wherever they need to go. Hybrid cloud allows data and apps to move smoothly, with cost-efficiency and security. You run each workload where it performs best on hybrid clouds.
Community cloud
Community cloud computing is a specialised cloud deployment model allowing multiple organizations, from the same industry or sector, to share a common cloud infrastructure. For organisations with shared goals, strict rules, and tight budgets, community cloud is the go-to option. Because it brings all the security, control, and collaboration, without high prices and with full autonomy. They each run their data, enforce their policies, but work together on a joint cloud backbone. And yes, you still get customization, full-on compliance with industry standards like HIPAA, FERPA, or PCI-DSS, and tight access controls.
What are the Types of Cloud Computing Services?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is the cloud model that lets you rent powerful compute resources, without buying a single server rack. It is an on-demand, scalable, pay-as-you-go model wherein the provider handles the hardware, data centers, and virtualization. Hence, you can focus on your OS, apps, and data. IaaS gives you flexibility and control over your IT resources, eliminating the need to procure, configure, or manage infrastructure.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
In PaaS, your provider handles the infrastructure, be it servers, networks, storage, OS, middleware, or dev tools. You don’t have to manage hardware or update the OS. With PaaS, you can easily collaborate with teammates, push updates in real time, and scale when traffic spikes. It is a cloud-powered momentum, built for devs who move fast and think big.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is a cloud-based software delivery model. It delivers applications through an internet browser, and the pricing is paid on a subscription or pay-as-you-use model. With SaaS, you are always on the latest version, patches, and updates handled seamlessly. Users subscribe to an app rather than purchasing it. The actual app runs on cloud servers. You leverage multi-tenant architecture with one app and many users. It is cost-effective, scalable, and mobile-friendly.
Function as a Service (FaaS)
FaaS is a cloud computing model, allows developers to run in response to specific events, without the headache of managing the infrastructure. Your function only runs when triggered, and you are billed only when it runs. FaaS allows cloud customers to deploy functionalities and just be charged for them when it is ultimately executed. It is stateless, short-lived, and scales easily. Functions run independently, which makes FaaS a suitable setup for microservices and real-time apps.
Conclusion
The Cloud is now, as it powers the present and future. From the remote IT environments to the Internet-based computing model, cloud computing frees you from physical limitations to unlock your full potential. With four dynamic service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, FaaS) and four deployment types (Public, Private, Hybrid, Community), you have a cloud fit for every need and budget. Of course, it comes with responsibilities, be it managing security, internet dependence, and cost control. But with best practices like data encryption, MFA, and access control, businesses can build trusted cloud frameworks with supreme confidence.